What is SOC? Installation, Operational Structure and Security
What is SOC? Installation, Operational Structure and Benefits to Data Security
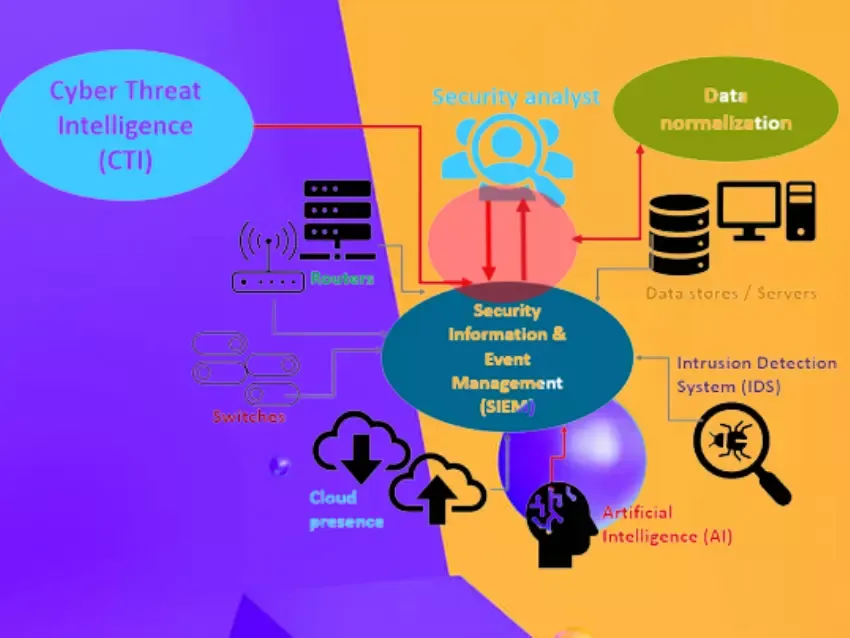
The Security Operations Center ( SOC) is a central unit in an enterprise responsible for monitoring, detecting, analyzing and responding to security threats. It helps ensure the confidentiality, integrity and availability of a business' critical assets and information systems. SOC uses a variety of security technologies such as intrusion detection/prevention systems, firewalls, security information and event management (SIEM) solutions to provide real-time security monitoring and threat detection.
How SOC Works
An SOC basically works in the following steps:
1. Monitoring
SOC collects and analyzes various security-related data and information from various sources such as logs from firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and servers.
2. Threat Detection
SOC uses a variety of security tools, such as intrusion detection systems and security information and event management (SIEM) solutions, to identify and warn of potential security threats.
3. Analysis
The SOC prioritizes and evaluates the severity of detected security events and determines the appropriate action plan.
4. Response
The SOC coordinates and executes the response to security incidents, which may include tasks such as isolating affected systems, containing the threat, and restoring normal operations.
5. Reporting
The SOC provides regular reports on the security status and security events to stakeholders such as management, auditors and regulators.
6. Continuous improvement
SOC continually reviews and improves processes and procedures to ensure they are effective in detecting and responding to new and evolving security threats.
Why is the Security Operations Center (SOC) Important?
SOC is important because:
- It provides centralized and continuous monitoring of security threats to a business.
- It facilitates the timely detection, analysis and response of security incidents.
- Improves the overall security posture of the business.
- It helps prevent, contain and mitigate security breaches.
- Helps maintain compliance with regulatory requirements and industry standards.
- It helps protect the confidentiality, integrity and availability of sensitive data and critical assets.
- It facilitates the sharing of security intelligence and information between different teams and departments within a business.
What Does the Security Operations Center do?
A Security Operations Center (SOC) performs the following tasks:
Real-time security monitoring and threat detection
Incident response and management
Vulnerability management and remediation
Compliance management and reporting
Security intelligence and threat analysis
Security incident management and log analysis
Malware analysis and threat prevention
Risk assessment and management
Penetration testing and security assessments
Safety awareness and training for employees
Continuous improvement of security processes and procedures
Key Roles in the SOC Team
The main roles in the SOC team are as follows:
1. Event responder
Configures and monitors security tools; prioritizes and classifies threats.
2. Security researcher
Identifies affected hosts and devices, evaluates running and terminated processes, and performs threat analysis.
3. Advanced security analyst
It identifies unknown vulnerabilities, examines past threats, and assesses vendor and product health.
4. SOC manager
Manages the entire SOC team, communicates with the CISO, team leaders, managers and partners.
5. Security engineer and architect
It manages the overall security architecture, ensuring that the architecture is part of the development cycle.
Now that you know the different staff a SOC team has, you can select your SOC team members based on your needs and the size of your business.
Types of Security Operations Centers
There are two main types of Security Operations Centers (SOCs):
1. Internal SOC
An internal SOC is a dedicated in-house team within an organization responsible for managing the organization's security.
2. Managed SOC
Managed SOC is an outsourced service provided by a third-party vendor to manage the security of multiple clients. This type of SOC typically provides 24-hour security monitoring, incident response and threat analysis services.
Both types of SOCs have their own advantages and disadvantages, and organizations can choose the type of SOC that best suits their needs based on factors such as budget, complexity of the security environment, and security requirements.
SOC (Security Operation Center) Advantages
The advantages of having a Security Operations Center (SOC) include:
1. An improved security posture
SOC helps a business improve its overall security posture by continuously monitoring and responding to security threats.
2. Faster incident response
SOC responds to security incidents more quickly and effectively, minimizing the business impact of security breaches.
3. Advanced threat detection
SOC can use a variety of security technologies, such as intrusion detection systems and security information and event management (SIEM) solutions, to detect security threats more accurately and in real time.
4. Compliance management
SOC helps businesses maintain compliance with regulatory requirements and industry standards.
5. Cost savings
SOC helps businesses reduce overall security costs by centralizing security operations and reducing the number of point solutions.
6. Enhanced information sharing
SOC can facilitate the sharing of security intelligence and information between different teams and departments within a business.
7. Better risk management
SOC helps businesses assess and manage security risks more effectively. Thus, it can reduce the overall risk of your business.
SOC Setup
Security Operations Center (SOC) deployment refers to the process of installing and configuring a central unit responsible for monitoring and managing the security status of an enterprise. A basic SOC setup includes the following components:
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) system
Threat intelligence feeds
Security tools and technologies (e.g. firewalls, intrusion detection/prevention systems)
Security analyst workstations
Communication and collaboration tools (e.g. chat, email, incident response management platform)
Physical security measures (e.g. access controls, cameras)
Standard operating procedures (SOPs) and incident response plans
The purpose of an SOC installation is to provide a comprehensive view of the business's security posture and enable rapid response to potential threats.
Data Security Benefits of Security Operations Center
The data security benefits of the Security Operations Center (SOC) are as follows:
- Improved threat detection and response time
- Advanced protection for sensitive data
- Compliance with safety regulations and standards
- Centralized management of security incidents
- Better risk assessment and management
- Increased operational efficiency
- Improved collaboration between security teams
- Reduced security costs through automation
- Better decision making with real-time data analysis
- Improved overall security posture and reduced security risks
Most Asked Questions About SOC
1. Why do you need a security operations center?
It is essential for a business to protect its data and assets. At this point, an SOC can protect a network and make a business less vulnerable to cyber attacks.
2. What should an SOC monitor?
It should monitor all network traffic from both internal and external sources, including servers, databases, and routers.
3. What is the difference between NOC and SOC?
A network operations center (NOC) focuses on monitoring a network's uptime rather than cybersecurity threats.
4. What is the difference between SOC and SIEM?
Security information and event management (SIEM) is a network monitoring solution that provides alerts and network usage benchmarks that SOC teams can leverage.